Tattoos against diabetes
) has been known for more than several millennia, but still in modern avant-garde society there is no consensus on how to perceive this phenomenon and how to react to it in emotional and psychological terms. In ancient times, tattoos served as a sign of tribe, clan, totem, endowed with a magical-sacred connotation, served as an exotic ornament, indicated social affiliation. Then there was the trend that tattoos were strikingly beautiful. For example, the famous James Cook thought when he showed Europe the Great Omai in the 18th century - a Polynesian who became a living tattoo gallery. Later, tattoos were seen as a shocking challenge to society, such as the sensational Lady Viola, who flaunted in front of the public body portraits of six American presidents, Charlie Chaplin and other celebrities. But recently, as it turned out,
Tattoo indicator
Recently , the German Chemical Society ’s Angewandte Chemie published a study by scientists at the Technical University of Munich who could rightly claim a real revolution in endocrinology, which could make life much easier for patients with diabetes or diabetes. chronic kidney disease. A team of scientists has developed a so-called "medical tattoo" that changes color depending on changes in glucose, albumin and acidity ( pH ).
“People have changed their appearance by introducing pigments into the top layer of skin for more than 4,000 years. We have developed a functional cosmetic technology that combines the art of tattooing and colorimetric biosensors. Using tattoos for diagnostic rather than cosmetic purposes is a concept of the future. The technique is to introduce indicator substances into the tattoo instead of the usual pigment, where they will record changes in the concentration of metabolic substances directly, without any spatial distance or time delay and possibly a very long period, " said the study authors.
How does it work?
Glucose, albumin and acidity levels were chosen as the main indicators that most often signal disturbances in the normal functioning of the body.Albumin is the main protein found in serum, low levels indicate liver or kidney problems, and high levels indicate heart problems. Blood glucose levels should be constantly monitored in patients with diabetes mellitus who have impaired carbohydrate metabolism. And too high or too low acidity can be caused by a number of diseases. All three of these parameters are easy to determine as a result of a routine blood test, but it can only be done in the laboratory.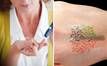 In particular, diabetics need to measure glucose levels regularly - sometimes several times a day (before each meal) - and for each such measurement you need to make an injection and take a drop of blood for analysis. According to the authors of the study, there are other, non-invasive methods (ie do not require blood sampling). For example, a special patch that measures the level of acidity and glucose in the blood by electrochemical analysis of sweat. However, they have a number of disadvantages, the main of which is the low accuracy of measurements.
In particular, diabetics need to measure glucose levels regularly - sometimes several times a day (before each meal) - and for each such measurement you need to make an injection and take a drop of blood for analysis. According to the authors of the study, there are other, non-invasive methods (ie do not require blood sampling). For example, a special patch that measures the level of acidity and glucose in the blood by electrochemical analysis of sweat. However, they have a number of disadvantages, the main of which is the low accuracy of measurements.
Nowonly one dye is designed perfectly (the one that determines the level of acidity), it can be used for continuous monitoring, as it returns to its original color after adjusting the chemical composition of the blood. According to scientists, other pigments can also be refined and made reusable.
In
addition to German scientists, American scientists are also interested in this latest diagnostic method. In particular, they have developed the technology of organic tattooing, when special live bacteria are added to ink paints, which are trained to respond to various factors not only of the human body but also the environment. This tattoo is applied to the skin using a 3D printerand bacteria can come into contact with each other, creating a whole computer on the skin and informing the owner about his health.
So, if scientists successfully complete their work, humanity, in addition to smart watches, smart bracelets, will be replenished with another smart device - a smart tattoo.
Author Kateryna Stebelska
Read also: The system of transplantation and donation in Ukraine - it is important to start talking
Tattoo indicator
Recently , the German Chemical Society ’s Angewandte Chemie published a study by scientists at the Technical University of Munich who could rightly claim a real revolution in endocrinology, which could make life much easier for patients with diabetes or diabetes. chronic kidney disease. A team of scientists has developed a so-called "medical tattoo" that changes color depending on changes in glucose, albumin and acidity ( pH ).
“People have changed their appearance by introducing pigments into the top layer of skin for more than 4,000 years. We have developed a functional cosmetic technology that combines the art of tattooing and colorimetric biosensors. Using tattoos for diagnostic rather than cosmetic purposes is a concept of the future. The technique is to introduce indicator substances into the tattoo instead of the usual pigment, where they will record changes in the concentration of metabolic substances directly, without any spatial distance or time delay and possibly a very long period, " said the study authors.
How does it work?
Glucose, albumin and acidity levels were chosen as the main indicators that most often signal disturbances in the normal functioning of the body.Albumin is the main protein found in serum, low levels indicate liver or kidney problems, and high levels indicate heart problems. Blood glucose levels should be constantly monitored in patients with diabetes mellitus who have impaired carbohydrate metabolism. And too high or too low acidity can be caused by a number of diseases. All three of these parameters are easy to determine as a result of a routine blood test, but it can only be done in the laboratory.
 In particular, diabetics need to measure glucose levels regularly - sometimes several times a day (before each meal) - and for each such measurement you need to make an injection and take a drop of blood for analysis. According to the authors of the study, there are other, non-invasive methods (ie do not require blood sampling). For example, a special patch that measures the level of acidity and glucose in the blood by electrochemical analysis of sweat. However, they have a number of disadvantages, the main of which is the low accuracy of measurements.
In particular, diabetics need to measure glucose levels regularly - sometimes several times a day (before each meal) - and for each such measurement you need to make an injection and take a drop of blood for analysis. According to the authors of the study, there are other, non-invasive methods (ie do not require blood sampling). For example, a special patch that measures the level of acidity and glucose in the blood by electrochemical analysis of sweat. However, they have a number of disadvantages, the main of which is the low accuracy of measurements. Nowonly one dye is designed perfectly (the one that determines the level of acidity), it can be used for continuous monitoring, as it returns to its original color after adjusting the chemical composition of the blood. According to scientists, other pigments can also be refined and made reusable.
In
addition to German scientists, American scientists are also interested in this latest diagnostic method. In particular, they have developed the technology of organic tattooing, when special live bacteria are added to ink paints, which are trained to respond to various factors not only of the human body but also the environment. This tattoo is applied to the skin using a 3D printerand bacteria can come into contact with each other, creating a whole computer on the skin and informing the owner about his health.
So, if scientists successfully complete their work, humanity, in addition to smart watches, smart bracelets, will be replenished with another smart device - a smart tattoo.
Author Kateryna Stebelska
Read also: The system of transplantation and donation in Ukraine - it is important to start talking